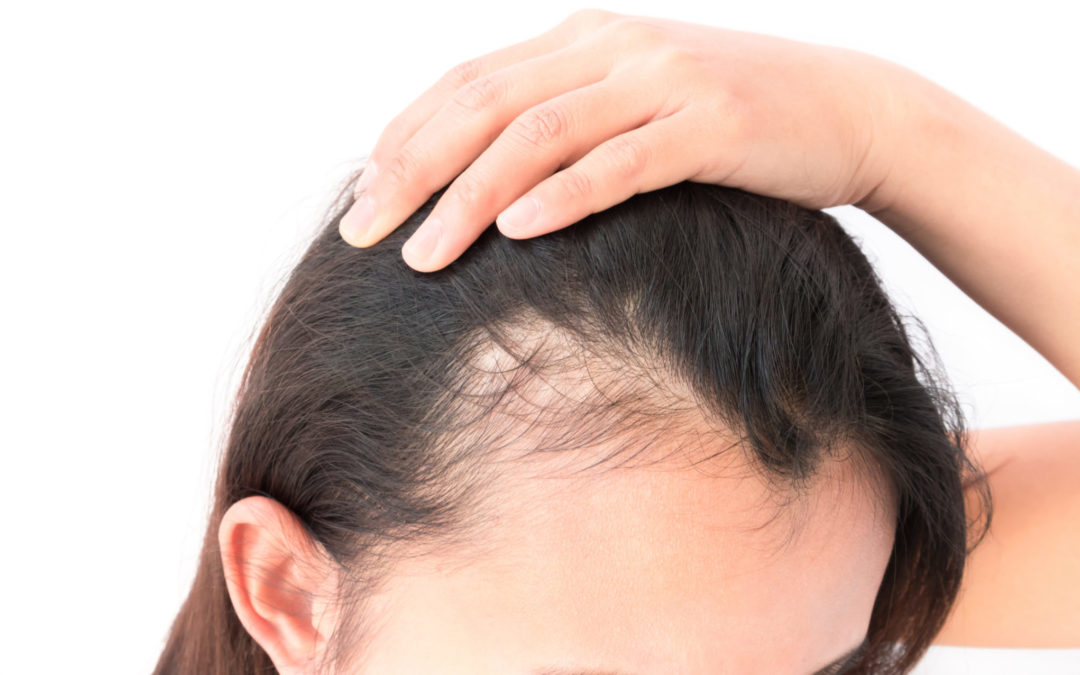
Vitamin B6, also known as pyridoxine, plays an indispensable role in the health and functionality of the body. This essential nutrient is involved in over 100 enzyme reactions, most of which are related to protein metabolism, making it a critical player in maintaining the health of our skin, eyes, liver, and, notably, hair. Beyond its cellular and metabolic functions, Vitamin B6 is crucial for brain development and function, and it helps the body make the hormones serotonin (which regulates mood) and norepinephrine (which helps your body cope with stress). Additionally, it’s instrumental in preventing and treating chronic diseases, including heart disease by controlling homocysteine levels in the blood, which can be a risk factor when elevated.
When it comes to hair health, Vitamin B6 holds a position of importance that cannot be overstated. Its role in protein metabolism extends to the keratin and melanin production for hair, which are essential for hair growth, strength, and color. Vitamin B6 helps in the prevention of dandruff, eczema, and psoriasis, ensuring that the scalp remains healthy, fostering an optimal environment for hair growth. Moreover, it aids in the absorption of zinc, a trace mineral that’s crucial for healthy hair follicle function. By contributing to the creation of hemoglobin in the blood, Vitamin B6 ensures that hair follicles receive enough oxygen, which is vital for stimulating hair growth and revitalizing the hair’s vitality and luster.
The significance of Vitamin B6 extends beyond its metabolic and physiological roles; it represents a beacon of hope for those battling hair loss or seeking to enhance their hair’s natural beauty and strength. This introduction to Vitamin B6’s general and hair-specific benefits sets the stage for a deeper exploration into how this vital nutrient can be optimized to support not only overall health but also the health and vibrancy of one’s hair.
What is Vitamin B6?
Vitamin B6, scientifically known as pyridoxine, is a water-soluble vitamin that is part of the B-vitamin family. It is essential for numerous physiological functions, playing a pivotal role in the body’s metabolism, brain function, and health maintenance. One of the unique aspects of Vitamin B6 is its involvement in the metabolism of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins and neurotransmitters. This means that Vitamin B6 is directly involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters such as serotonin, which affects mood, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which helps control brain function. Additionally, Vitamin B6 is vital for creating red blood cells and maintaining healthy blood sugar levels, showcasing its broad impact on overall health.
Vitamin B6 exists in several forms, including pyridoxine, pyridoxal, pyridoxamine, and their phosphorylated forms: pyridoxine phosphate, pyridoxal phosphate (PLP), and pyridoxamine phosphate. Pyridoxal phosphate, in particular, is the active form of Vitamin B6 and serves as a coenzyme in many enzyme reactions in the body, primarily involving amino acid metabolism. These forms of Vitamin B6 are interconvertible in the body, ensuring that the vitamin can perform its various roles effectively.
The sources of Vitamin B6 are diverse, allowing for its intake from different foods as part of a balanced diet. It is found in a wide range of foods, including poultry, such as chicken and turkey, which are among the richest sources. Fish, such as salmon and tuna, also contain high levels of Vitamin B6. Additionally, Vitamin B6 can be found in whole grains, cereals, nuts, beans, bananas, and some vegetables like carrots and spinach. Fortified foods, including some breakfast cereals, can also be significant sources of Vitamin B6, ensuring that individuals can meet their daily dietary requirements.
Given its water-soluble nature, Vitamin B6 cannot be stored by the body and must be consumed regularly to maintain adequate levels. Its widespread availability in various food sources makes it accessible for most people, although certain health conditions and lifestyle choices may necessitate supplementation under medical guidance. The role of Vitamin B6 in the body is undeniably crucial, not only for its direct impact on metabolic and neurological functions but also for its indirect role in supporting overall health through nutrient metabolism and synthesis.
The Role of Vitamin B6 in Hair Health
Vitamin B6 plays a crucial role in maintaining and enhancing hair health, influencing hair growth, strength, and vitality from the cellular level. Its contribution to hair health is multifaceted, primarily through its involvement in protein metabolism, which is essential for the formation of new hair cells and the maintenance of hair growth.
Contribution to Hair Growth and Strength
Vitamin B6 aids in hair growth and strength in several key ways:
- Protein Synthesis: Given that hair is primarily made of keratin, a type of protein, Vitamin B6’s role in protein metabolism is critical. It aids in the synthesis of keratin, ensuring that hair grows strong and resilient.
- Hemoglobin Production: Vitamin B6 is vital for the production of hemoglobin in the blood, which is responsible for transporting oxygen to cells, including hair follicles. Adequate oxygenation of hair follicles is crucial for stimulating hair growth and maintaining the health of the hair.
- Regulation of Androgens: Androgens, such as testosterone, can negatively affect hair growth when present in imbalanced amounts. Vitamin B6 helps in the regulation of androgen levels, thereby reducing the risk of hair loss associated with hormonal imbalances.
Relationship with Other Nutrients
The benefits of Vitamin B6 for hair health are further enhanced when considered in conjunction with other nutrients, particularly Vitamin B12 and folic acid, which work synergistically to promote healthy hair:
- Vitamin B12: Like Vitamin B6, Vitamin B12 is crucial for the health of red blood cells and for keeping hair follicles well-oxygenated. A deficiency in Vitamin B12 can lead to hair loss, underscoring the importance of maintaining adequate levels of both vitamins for optimal hair health.
- Folic Acid: Folic acid, another B vitamin, plays a critical role in cell growth and division, which is essential for the natural growth cycle of hair. It works alongside Vitamin B6 and B12 to support the metabolism of amino acids and the synthesis of DNA, which is necessary for the formation of new hair cells.
The interplay between Vitamin B6, B12, and folic acid is a testament to the complexity of hair health, highlighting the need for a comprehensive approach to nutrition that supports the body’s various biological processes. Adequate intake of these vitamins ensures not only the promotion of hair growth but also the prevention of hair loss, contributing to the overall strength and vitality of the hair.
In summary, Vitamin B6’s contribution to hair health is significant and multifaceted, encompassing the promotion of hair growth, the strengthening of hair, and the regulation of factors that could otherwise impair hair health. Its effectiveness is maximized when combined with other essential nutrients, underscoring the importance of a balanced diet for maintaining not just healthy hair, but overall wellbeing.
Scientific Evidence on Vitamin B6 and Hair
The relationship between Vitamin B6 and hair health has been the subject of numerous scientific studies, which have explored how this essential nutrient influences hair growth, quality, and preservation. These investigations have provided valuable insights, affirming the positive impact of Vitamin B6 on hair health.
Summary of Research Findings
Research findings have consistently supported the notion that Vitamin B6 plays a vital role in promoting hair health through various mechanisms:
- Enhanced Hair Growth: Studies have shown that Vitamin B6, due to its critical role in protein metabolism and red blood cell production, can significantly contribute to the growth of healthy hair by ensuring that hair follicles receive adequate oxygen and nutrients.
- Improved Hair Quality: Vitamin B6 has been linked to the improvement in hair quality, including its strength and texture. By participating in the synthesis of keratin, Vitamin B6 helps in enhancing the structural integrity of hair, making it less prone to breakage and damage.
- Preservation of Hair Color: Some research suggests that Vitamin B6 may play a role in preserving hair color by aiding in the formation of melanin, which imparts pigment to the hair.
Case Studies or Clinical Trials
While specific case studies or clinical trials focusing solely on Vitamin B6 and its direct effects on hair are relatively scarce, several broader nutritional studies have included Vitamin B6 as part of a complex of vitamins and minerals assessed for their benefits on hair health:
- Clinical Trials on Nutritional Supplements: Some clinical trials have examined the effects of multivitamin and mineral supplements, including Vitamin B6, on hair health. These studies have often reported improvements in hair growth and reductions in hair loss among participants, suggesting a synergistic effect of Vitamin B6 when combined with other nutrients.
- Studies on Vitamin B6 and Hormonal Balance: Research into the effects of Vitamin B6 on hormonal balance, particularly its role in regulating androgen levels, has indirect implications for hair health. By mitigating the impact of hormones that can cause hair thinning and loss, Vitamin B6 contributes to maintaining a fuller, healthier head of hair.
Implications of Research
The scientific evidence points to a clear link between adequate intake of Vitamin B6 and improved hair health. However, it also underscores the complexity of hair growth processes and the interplay of various nutrients, highlighting that optimal hair health is best achieved through a holistic approach to nutrition and wellness.
While direct clinical evidence specifically highlighting Vitamin B6’s isolated effects on hair might be limited, the cumulative research findings support the inclusion of Vitamin B6 as a key component of a diet aimed at promoting healthy hair. Future studies are likely to further elucidate the specific mechanisms through which Vitamin B6 affects hair growth and quality, offering more targeted insights for nutritional recommendations and potential treatments for hair-related conditions.
Signs of Vitamin B6 Deficiency Related to Hair
Vitamin B6 deficiency, while relatively rare, can lead to several noticeable symptoms, including some that specifically affect hair health. Identifying these signs early can help in addressing the deficiency before it leads to more severe health issues.
Symptoms Indicating a Vitamin B6 Deficiency
Hair-Related Issues
- Hair Loss: One of the more noticeable signs of Vitamin B6 deficiency is hair loss. Given Vitamin B6’s role in protein metabolism and red blood cell production, a deficiency can result in inadequate nutrient and oxygen delivery to hair follicles, hindering their ability to produce new hair.
- Brittle Hair: Hair that becomes unusually brittle and prone to breaking may also indicate a lack of sufficient Vitamin B6. This vitamin is crucial for the formation of keratin, a protein that gives hair its structure and strength. Without adequate Vitamin B6, hair might lose its resilience.
- Dandruff and Scalp Issues: Vitamin B6 deficiency can lead to seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff. A healthy scalp is essential for healthy hair growth, and without enough Vitamin B6, individuals may experience an itchy, flaky scalp, which can exacerbate hair loss.
Broader Health Implications
Beyond hair health, Vitamin B6 deficiency can manifest in several other physical and psychological symptoms, underscoring the importance of this nutrient across various bodily functions:
- Skin Problems: Similar to its effects on hair, a Vitamin B6 deficiency can lead to skin issues, such as rashes or cracks around the mouth and lips (cheilosis).
- Fatigue and Low Energy: Given its role in hemoglobin production and energy metabolism, a lack of Vitamin B6 can result in feelings of fatigue and a general lack of energy.
- Weakened Immune Function: Vitamin B6 is vital for immune health. Deficiency may lead to a weakened immune response, making the body more susceptible to infections.
- Mood Changes: Vitamin B6 is necessary for the synthesis of neurotransmitters that regulate mood, including serotonin and dopamine. Deficiency can lead to mood swings, depression, and anxiety.
- Cognitive Decline: There is evidence to suggest that Vitamin B6 plays a role in cognitive health, with deficiency potentially leading to confusion and a decrease in cognitive function.
Addressing Vitamin B6 Deficiency
Recognizing these symptoms as potential signs of Vitamin B6 deficiency is the first step toward addressing any underlying nutritional gaps. For those experiencing hair-related issues alongside other symptoms of deficiency, consulting a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan is crucial. Dietary adjustments to include more Vitamin B6-rich foods or, in some cases, supplementation under medical guidance, can effectively rectify the deficiency, improving hair health and overall well-being.
Sources of Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6 is abundantly available in a variety of foods, ensuring that with a well-planned diet, individuals can meet their daily requirements for this essential nutrient, supporting not only hair health but also overall well-being.
Comprehensive List of Vitamin B6-Rich Foods
Animal Sources
- Poultry: Chicken and turkey are excellent sources of Vitamin B6, providing a significant portion of the daily requirement in a single serving.
- Fish: Certain types of fish, including salmon, tuna, and halibut, are rich in Vitamin B6, offering both this vital nutrient and omega-3 fatty acids beneficial for hair health.
- Beef Liver: Liver is one of the most concentrated sources of Vitamin B6, packed with other essential nutrients like Vitamin A, which is also crucial for skin and hair health.
- Eggs: A versatile and accessible source, eggs contain Vitamin B6 along with biotin, another B-vitamin important for healthy hair.
Plant Sources
- Chickpeas: A staple in many diets, chickpeas (garbanzo beans) are a great vegetarian source of Vitamin B6, making them a valuable addition to salads, soups, and hummus.
- Bananas: This fruit is not only an easy snack but also a good source of Vitamin B6, potassium, and carbohydrates.
- Spinach: Leafy greens like spinach are packed with Vitamin B6, folate, iron, and magnesium, all of which contribute to hair health.
- Sweet Potatoes: A nutrient-dense vegetable that provides Vitamin B6, sweet potatoes are also high in beta-carotene, which the body converts into Vitamin A.
- Avocados: Rich in Vitamin B6, avocados also offer healthy fats that are beneficial for the skin and hair.
- Nuts and Seeds: Certain nuts and seeds, including walnuts, sunflower seeds, and pistachios, are good sources of Vitamin B6 and other nutrients essential for healthy hair.
Recommendations for Daily Intake
The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for Vitamin B6 varies by age, gender, and other factors such as pregnancy and breastfeeding. For most adults, the RDA is set at 1.3 milligrams per day. However, this amount can increase to 1.5 milligrams per day for women over 50 and 1.7 milligrams per day for men over 50. Pregnant and breastfeeding women require slightly more, around 1.9 milligrams and 2.0 milligrams per day, respectively.
To support hair health and overall well-being, incorporating a variety of Vitamin B6-rich foods into your diet is key. Since Vitamin B6 is involved in numerous bodily functions beyond hair growth, meeting the daily recommended intake is crucial for maintaining optimal health. For individuals concerned about their hair health or those experiencing symptoms of Vitamin B6 deficiency, consulting with a healthcare provider may be beneficial. They can offer guidance on dietary choices and determine if supplementation might be necessary to achieve the desired levels of Vitamin B6.
Supplementation and Hair Health
Supplementing with Vitamin B6 can be a strategic approach to enhancing hair health, particularly for individuals who may not be able to meet their nutritional needs through diet alone. However, navigating the world of supplements requires an understanding of when such intervention is appropriate, as well as awareness of potential side effects and necessary precautions.
Guidelines on When to Consider Vitamin B6 Supplements
- Dietary Restrictions: Individuals with dietary restrictions, such as vegans or those with certain food allergies, might find it challenging to obtain adequate Vitamin B6 from their diet alone and may benefit from supplementation.
- Symptoms of Deficiency: Signs of Vitamin B6 deficiency, including hair loss, brittle hair, and a scaly rash on the scalp or face, can indicate the need for supplements after consultation with a healthcare provider.
- Health Conditions: Certain health conditions, including kidney diseases, autoimmune disorders, and malabsorption syndromes, can impair the body’s ability to absorb Vitamin B6, making supplementation necessary.
- Medication Interactions: Some medications, such as oral contraceptives and certain anti-seizure drugs, can deplete the body’s Vitamin B6 levels. Individuals on these medications may require supplements to counteract these effects.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
While Vitamin B6 supplements can be beneficial, they are not free from potential side effects, especially when taken in high doses or without medical supervision.
- Neurological Symptoms: Excessive intake of Vitamin B6, particularly at doses exceeding 100 mg per day, can lead to nerve damage, causing symptoms such as numbness and pain in the limbs. This condition is typically reversible upon discontinuation of the supplement.
- Interactions with Medications: Vitamin B6 can interact with certain medications, including some anticonvulsants, potentially affecting their efficacy. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting Vitamin B6 supplements if you are on prescribed medications.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: High doses of Vitamin B6 may cause gastrointestinal symptoms, including nausea, stomach pain, and heartburn.
- Sensitivity and Allergy: Although rare, some individuals may experience allergic reactions to Vitamin B6 supplements, manifesting as skin rashes, itching, or difficulty breathing.
The recommended daily upper intake level for Vitamin B6 in adults is set at 100 mg to prevent the risk of adverse effects. It’s crucial to adhere to this guideline and consult with a healthcare professional before beginning any supplement regimen, especially for long-term use.
In summary, Vitamin B6 supplementation can be a valuable tool for improving hair health and addressing deficiencies, but it should be approached with caution. Adequate knowledge of when to supplement, potential side effects, and the importance of professional guidance ensures that supplementation contributes positively to overall health and wellness, including the vitality and strength of your hair.
Practical Tips for Boosting Vitamin B6 Intake
Boosting your Vitamin B6 intake through dietary choices is a practical and natural way to enhance hair health and overall well-being. Here are some dietary tips and meal ideas designed to increase your Vitamin B6 consumption, alongside a discussion on maintaining a balanced nutrient intake for optimal hair health.
Dietary Tips for Increasing Vitamin B6 Consumption
- Incorporate B6-Rich Foods into Every Meal: Aim to include at least one source of Vitamin B6 in each meal. For breakfast, consider eggs or fortified cereals. Lunch and dinner can include poultry, fish, or legumes, accompanied by B6-rich vegetables like spinach or sweet potatoes.
- Snack on Nuts and Seeds: Walnuts, sunflower seeds, and pistachios are not only great snacks but also excellent sources of Vitamin B6. They can be added to yogurts, salads, or eaten alone for a midday boost.
- Use Avocado as a Spread: Avocados are a versatile source of Vitamin B6 that can be used as a spread on toast or blended into smoothies for an extra nutrient kick.
- Explore International Cuisines: Many international dishes are rich in Vitamin B6, such as hummus (made from chickpeas), guacamole (made with avocados), and various fish dishes. Exploring different cuisines can make increasing your Vitamin B6 intake both delicious and adventurous.
Meal Ideas to Boost Vitamin B6 Intake
- Breakfast: A smoothie with bananas, spinach, and a scoop of whey protein; or oatmeal topped with walnuts and sliced bananas.
- Lunch: Quinoa salad with chickpeas, avocado, and a variety of vegetables; or a turkey and spinach wrap.
- Dinner: Grilled salmon with a side of roasted sweet potatoes and steamed broccoli; or chicken stir-fry with bell peppers, garlic, and brown rice.
Balancing Nutrient Intake for Optimal Hair Health
While increasing Vitamin B6 intake is beneficial for hair health, it’s important to maintain a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrients:
- Protein: Hair is primarily made of protein, so adequate protein intake is essential for hair growth and strength. Include lean meats, fish, beans, and nuts in your diet.
- Iron: Iron deficiency is a common cause of hair loss. Incorporate iron-rich foods like spinach, lentils, and fortified cereals.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: These healthy fats are important for hair hydration and scalp health. Sources include fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Other vitamins and minerals, such as Vitamin C (for collagen production), Vitamin E (for scalp circulation), and zinc (for hair follicle health), are also crucial. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds can provide these essential nutrients.
By integrating a wide range of nutrients into your diet and focusing on Vitamin B6-rich foods, you can support not only your hair health but also enhance your overall nutritional well-being. Remember, a balanced and varied diet is the key to unlocking the full potential of your hair’s health and beauty.
The Interplay of Vitamin B6 and Lifestyle Factors on Hair Health
The health of your hair is not solely dependent on the nutrients you consume but is also significantly influenced by your overall lifestyle. Factors such as diet, stress management, and sleep patterns play a crucial role in determining the levels of Vitamin B6 in your body and, by extension, the health and vitality of your hair. Understanding the interplay between Vitamin B6 and these lifestyle factors can help you make informed choices to support hair growth and health.
Impact of Lifestyle Choices on Vitamin B6 Levels and Hair Health
Diet
A balanced diet rich in Vitamin B6 and other essential nutrients is foundational to hair health. Processed foods and those high in sugar can lead to nutrient deficiencies, including Vitamin B6, affecting hair growth and quality. Conversely, a diet emphasizing whole foods, with plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, can boost your Vitamin B6 levels and promote healthier hair.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can deplete your body of Vitamin B6, as it can increase the requirement for this vitamin due to its role in neurotransmitter synthesis and stress response regulation. High stress levels can also lead to hair loss or thinning by affecting the hair growth cycle. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or regular exercise can help manage stress and support hair health.
Sleep Patterns
Adequate sleep is essential for the regeneration and repair of body tissues, including hair follicles. Poor sleep can affect hormone levels, including cortisol, which can indirectly impact hair health by exacerbating stress and potentially affecting Vitamin B6 metabolism. Ensuring you get enough restorative sleep each night is critical for maintaining healthy hair.
Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle That Supports Hair Growth and Health
- Prioritize Whole Foods: Focus on a diet that includes Vitamin B6-rich foods, such as poultry, fish, fortified cereals, and a variety of fruits and vegetables, to support hair health.
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate water intake is essential for maintaining the health of your hair follicles and scalp. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water a day.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular physical activity can help reduce stress, improve sleep, and increase blood circulation to the scalp, promoting hair growth and health.
- Manage Stress: Engage in stress-reduction activities that you enjoy, whether it’s reading, taking walks, practicing mindfulness, or pursuing hobbies.
- Get Enough Sleep: Ensure you’re getting 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to support your body’s natural repair processes, which include those that affect hair health.
- Limit Heat Styling and Chemical Treatments: These can damage hair, leading to breakage and loss. When possible, let your hair air-dry and embrace its natural texture.
- Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol Consumption: Both can contribute to hair loss and negatively affect overall health, including the levels of essential nutrients like Vitamin B6.
By integrating these lifestyle choices into your daily routine, you can create an environment that supports not just the health of your hair but your overall well-being. A holistic approach that includes proper nutrition, stress management, and healthy habits is key to maintaining vibrant, healthy hair and optimizing your body’s Vitamin B6 levels.
FAQs on Vitamin B6 and Hair Health
What are the best natural sources of Vitamin B6?
The best natural sources of Vitamin B6 include poultry (such as chicken and turkey), fish (especially salmon, tuna, and halibut), beef liver, eggs, and a variety of fruits and vegetables like bananas, avocados, and spinach. Legumes, such as chickpeas, and certain nuts and seeds are also excellent sources of Vitamin B6, making it accessible to both meat-eaters and vegetarians alike.
What signs indicate a Vitamin B6 deficiency?
Signs of Vitamin B6 deficiency can manifest as both general and hair-specific symptoms. Hair-related signs include increased hair loss, brittle hair, and potentially dandruff or a scaly rash on the scalp. General symptoms may involve fatigue, irritability, muscle pains, and changes in mood. Because Vitamin B6 is crucial for the proper function of various bodily systems, deficiency symptoms can be quite broad.
Is it safe to take Vitamin B6 supplements?
Yes, it is generally safe to take Vitamin B6 supplements, especially when done under the guidance of a healthcare professional. However, it’s important to adhere to the recommended dietary allowance (RDA) and not exceed the upper intake levels, as high doses of Vitamin B6 can lead to adverse effects, such as neurological symptoms like numbness and coordination issues. The recommended upper limit for adults is 100 mg per day.
Can Vitamin B6 supplements improve hair growth?
Vitamin B6 supplements can contribute to improved hair growth, particularly in individuals who have a deficiency or are at risk of developing one due to dietary restrictions, certain health conditions, or medication use. By supporting protein metabolism, hemoglobin production, and the regulation of hormones, Vitamin B6 can positively affect hair health. However, supplementation should be part of a holistic approach to hair care, including a balanced diet and proper hair and scalp maintenance.
How much Vitamin B6 do I need daily for healthy hair?
The amount of Vitamin B6 needed daily depends on age, sex, and other individual factors. For most adults, the RDA for Vitamin B6 is 1.3 mg, with slightly higher needs for adults over 50 (1.7 mg for men and 1.5 mg for women) and for pregnant or breastfeeding women (1.9 mg and 2.0 mg, respectively). While these recommendations aim to prevent deficiency, maintaining this level of intake is also beneficial for hair health.
Can too much Vitamin B6 cause hair loss?
There is no direct evidence to suggest that excessive intake of Vitamin B6 causes hair loss. However, taking very high doses of Vitamin B6 supplements can lead to side effects, including neurological symptoms. Hair health can be influenced by a wide range of factors, including nutrient imbalances, so maintaining a balanced and moderate approach to supplementation is key.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Vitamin B6 stands out as a critical nutrient with significant benefits for hair health, including promoting hair growth, enhancing hair strength, and maintaining a healthy scalp. Its role in protein metabolism, red blood cell production, and hormone regulation directly impacts the vitality and resilience of hair, making it an essential component of any hair care regimen.
The key benefits of Vitamin B6 for hair underscore the importance of a well-rounded diet rich in this vital nutrient. From preventing hair loss to ensuring the lusciousness and strength of your locks, Vitamin B6 plays a pivotal role that cannot be overlooked. Whether through the consumption of poultry, fish, fruits, and vegetables, or through supplementation when necessary, maintaining adequate levels of Vitamin B6 is paramount for supporting hair health.
As we navigate the complexities of maintaining healthy hair, it becomes evident that a holistic approach is not just beneficial but necessary. Considering your Vitamin B6 intake in the context of overall nutrition and lifestyle choices offers a comprehensive strategy for enhancing hair health. This includes balancing your diet, managing stress, ensuring adequate sleep, and adopting hair care practices that minimize damage.
We encourage readers to view their Vitamin B6 intake as a crucial part of a broader hair care and health maintenance plan. By doing so, you not only support the health and beauty of your hair but also contribute to your overall well-being. Remember, healthy hair is a reflection of a healthy body, and adequate Vitamin B6 intake is a key piece of that puzzle.